The ISO 14001 requirements are a series of protocols, measures, controls, procedures, and auditing methods set out to help organizations identify, monitor, manage, control, and improve their immediate environmental issues with a more holistic approach. The emphasis is waste reduction.
Contents
There are mandatory and non-mandatory requirements; to find out which of the requirements you should document, please continue reading.

At the core of the standard are the first 3 clauses that deal with the terms and definitions, the scope of the standard and the standard's references. There are no requirements in the first 3 clauses but they do provide a deeper understanding of the intent and the terminology used throughout.
Clauses 4 to 10 document the ISO 14001 requirements that any business needs to set up and manage their EMS.
All of the ISO 14001 requirements are fully-documented and explained in our Environmental Management System Template.

Maintain the following as a type of ‘documented information'
| Clause | Maintain the following as a type of documented information Clause |
| 4.3 | The scope of the environmental and EMS |
| 4.4 | Information necessary to support the operation of processes |
| 5.2 | Environmental policy |
| 6.1.1 | Risk and opportunities that need to be addressed |
| 6.1.2 | EMS aspects and impacts, and hazards and risks, and their criteria to determine significance |
| 6.1.3 | Information about an organization’s compliance obligations |
| 6.2 | Environmental objectives |
| 7.5.1a | Documented information required by 14001:2015, refer to the 'Retain' table below |
Retain the following as a type of ‘documented information'
| Clause | Retain the following as a type of documented information as a record |
| 4.4 | Documented information to the extent necessary to have confidence that the EMS processes are being carried out as planned |
| 7.1.5.1 | Evidence of fitness for purpose of monitoring and measuring resources |
| 7.1.5.2 | Evidence of the basis used for calibration of the monitoring and measurement resources (when no international or national standards exist) |
| 7.2 | Evidence of competence of people doing work under the control of the organization that affects the performance and effectiveness of the EMS |
| 7.4.1 | Evidence of communications to external parties and interested parties |
| 7.5.1b | Documented information required by the EMS |
| 8.2.3 | Results of the review and new requirements for the products and services |
| 8.3.2 | Records to demonstrate compliance with design and development requirements |
| 8.3.3 | Records of design and development inputs |
| 8.3.4 | Records of the activities of design and development controls |
| 8.3.5 | Records of design and development outputs |
| 8.3.6 | Design and development changes, including the results of the review and the authorization of the changes and necessary actions |
| 8.4.1 | Records of the evaluation, selection, monitoring of performance and re-evaluation of external providers and any actions arising |
| 8.5.2 | Evidence of the unique identification of outputs when traceability is a requirement |
| 8.5.3 | Records of property of the customer or external provider that is lost, damaged or non-conforming and of its communication to the owner |
| 8.5.6 | Results of the review of changes for production or service provision, the persons authorizing the change, and necessary actions taken |
| 8.6 | Records of authorized release of products for delivery to the customer including acceptance criteria and traceability to the authorizing person(s) |
| 8.7 | Records of non-conformities, actions taken, concessions and the identity of the authority deciding the action in respect of the nonconformity |
| 9.1.1 | Evidence of the evaluation of the performance and the effectiveness of the EMS |
| 9.1.2 | Evidence of compliance evaluations |
| 9.2.2 | Evidence of the implementation of the internal audit programme |
| 9.2.2 | Evidence of internal audit results |
| 9.3.3 | Evidence of the results of management reviews |
| 10.2.2 | Evidence of the nature of the non-conformities |
| 10.2.2 | Evidence of any subsequent actions taken to correct non-conformities |
| 10.2.2 | Results of any corrective actions |
All of the ISO 14001 requirements are fully-documented and explained in our Environmental Management System Template.
These types of documented information will demonstrate that your environmental management system is effective and is providing value for the environment.
Certification to the ISO 14001:2015 standard will help embed a culture of sustainability and allow any business to enhance their environmental performance, meet their compliance obligations, and achieve their environmental objectives.

Based upon the requirements of ISO 14001:2015, an environmental management system (EMS) is a structured, organised method for controlling and reducing the environmental impact of your business’s operations and is a practical tool that helps organisations understand and manage their impacts on the environment.
An EMS should be designed and implemented to function within current business practices and serves as an effective tool to help your business grow and improve.
ISO 14001 will also help you to focus on satisfying the expectations of customers, the needs of supply chains, employees, and end-users, whilst meeting regulatory requirements.
Your EMS will act as a framework that enables the continual improvement of environmental performance by managing negative impacts and helping to increase resource efficiency, through which organisations can engage with their employees, customers, clients and other stakeholders.
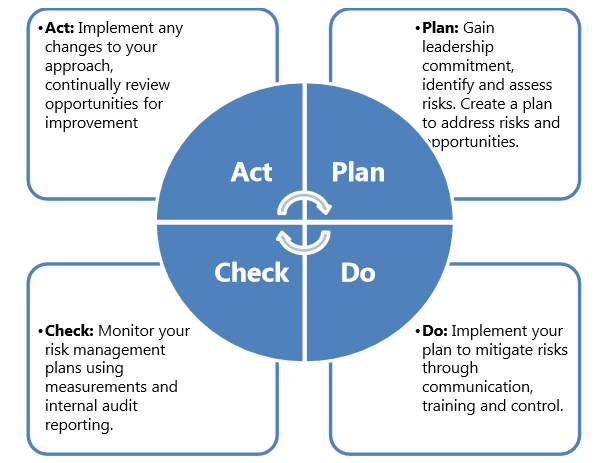
Critical to the EMS operation is the PDCA cycle or Plan/Do/Check/Act cycle.
The PDCA cycle is recognized by ISO as an approved management methodology and is compulsory within the scope of ISO 14001.
All of the ISO 14001 requirements are fully-documented and explained in our Environmental Management System Template (EMS).
We have procedures, templates, checklists, process maps, forms and gap analysis tools to help your documentation without missing a single input or output.
Before you invest all the hours reinventing the wheel, before you spend countless dollars outsourcing the task — try our templates.
Updated: 9th May 2022
Author: Richard Keen

Richard is our Compliance Director, responsible for content & product development.
But most importantly he is ISO's biggest fanboy and a true evangelist of the standards.
Learn more about Richard

Don’t Try to Manage It All Alone!
Our ISO Auditors and Quality Manager Trainers have been in this industry for years, and since 2002 we’ve been providing thousands of small businesses and large corporations with the tools they need to get certified.
Instead of trying to create everything you need to follow this process from scratch, use ours. We have procedures, templates, checklists, process maps, forms and gap analysis tools to help your documentation without missing a single input or output.
Before you invest all the hours reinventing the wheel, before you spend countless dollars outsourcing the task — try our templates.